
Speech Activity Detection
The goal in the SAD task is to automatically detect the presence of speech segments in an audio recordings of variable duration. A system output is scored by comparing the system produced start and end times of speech and non-speech segments in audio recordings to human annotated start and end times. The DCF( Detection Cost Function)) is a function of false-positive (false alarm) and false-negative (missed detection) rates calculated from comparison to the human annotation that will be the reference for the comparison.
Instructions
Performance Metrics
Four system output possibilities are considered:
- True Positive (TP) - system correctly identifies start-stop times of speech segments compared to the reference (manual annotation)
- True Negative (TN) - system correctly identifies start-stop times of non-speech segments compared to reference,
- False Positive (FP) - system incorrectly identifies speech in a segment where the reference identifies the segment as non-speech
- False Negative (FN) - system missed identification of speech in a segment where the reference identifies a segment as speech.
SAD error rates represent a measure of the amount of time that is misclassified by the systems segmentation of the test audio files. Missing, or failing to detect, actual speech is considered a more serious error than misidentifying its start and end times.
The four system output possibilities mentioned above determine the probability of a false positive (PFP) and the probability of a false negative (PFN). Developers are responsible for determining a hypothetical optimum setting (θ) for their system that minimizes the DCF value.
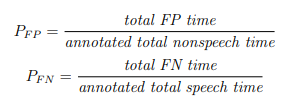
PFP = detecting speech where there is no speech, also called a false alarm. PFN = missed detection of speech, i.e., not detecting speech where there is speech, also called a miss
DCF(θ) is the detection cost function value for a system at a given system decision-threshold setting.
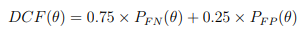
PFN and PFP are weighted 0.75 and 0.25, respectively, θ - denotes a given system decision-threshold setting.
Baseline
For information about FSC - Phase 2 baseline results, Pleaseclick here.
Baseline systems will be announced soon!
References
Coming soon!.
